-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

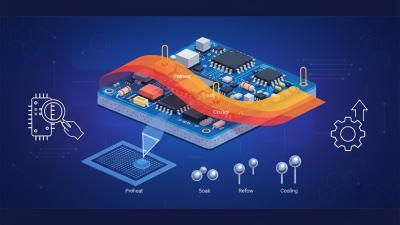
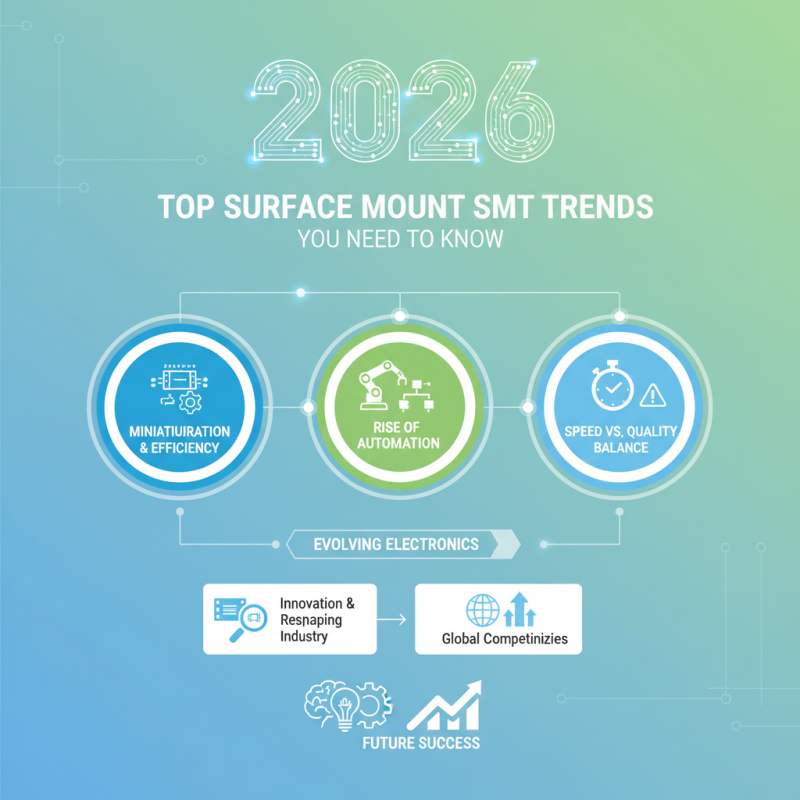
As we look towards 2026, the world of electronics is evolving rapidly. The innovation in Surface Mount Smt technology is reshaping our industry. New trends are emerging that could change the way we approach designs and production.
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on efficiency and miniaturization. This shift enhances product performance while reducing costs. The rise of automation in Surface Mount Smt processes is also noteworthy. It aims to streamline workflows and minimize human error.
However, not all advancements come without challenges. The push for speed can sometimes compromise quality. Companies need to reflect on balancing these factors. It's crucial to keep an eye on these trends to remain competitive in the market. Understanding Surface Mount Smt's future will be essential for success.
Surface mount technology (SMT) is evolving rapidly. In 2026, we will see significant innovations that could transform the industry. One key trend is the integration of artificial intelligence in manufacturing processes. AI can streamline production, making it more efficient. This may reduce errors but also raises concerns about potential job losses.
Another innovation is the miniaturization of components. As devices become smaller, manufacturers face challenges. They must ensure reliability while maintaining performance. This could lead to a new range of materials. Conductive inks and nano-coatings may play a crucial role here. However, the long-term effects of these innovations on durability are still uncertain.
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important. Companies are exploring eco-friendly materials for SMT. While this is a positive trend, the real impact will depend on widespread adoption. Many organizations still struggle to balance cost and environmental responsibility. As the industry moves forward, these challenges will need careful reflection.
Emerging materials play a crucial role in shaping SMT applications. As technology advances, new materials offer better performance and efficiency. For instance, advanced polymers are gaining popularity due to their lightweight and flexibility. These properties are essential for compact designs in electronic devices.
However, the integration of these materials isn't without challenges. Certain polymers can be difficult to bond with traditional solder pastes. This leads to potential reliability issues over time. Engineers must carefully select materials to ensure long-term performance. Cost is also a concern; high-quality materials can drive up production expenses.
Consideration of environmental impact is necessary. Biodegradable materials are rising, but they often lack durability. Striking a balance between sustainability and functionality is not easy. Future SMT applications must address these complexities to succeed in a rapidly evolving market.
This bar chart illustrates the projected adoption rate of emerging materials in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) applications by 2026. As the industry evolves, new materials play a crucial role in improving performance and efficiency.
Automation and robotics are reshaping Surface Mount Technology (SMT) processes significantly. According to a recent report by the Electronics Industry Association, about 75% of manufacturers are investing in automation for SMT lines. This shift leads to improved efficiency but also raises concerns about job displacement.
With the growing demand for faster production rates, robotics play a crucial role. Automated pick-and-place machines can operate 24/7, drastically reducing production times. However, integrating these technologies isn't always smooth. Many companies face challenges related to software compatibility and workforce retraining. In fact, nearly 60% of companies reported difficulties in adjusting their existing infrastructure to accommodate automation.
Moreover, the evolving complexity of products means that not all processes can be easily automated. Some assembly tasks still require human intervention to ensure quality and precision. This blend of technology and human skill creates a unique challenge. Striking the right balance is essential for a successful transition to automated SMT processes. As the industry moves forward, continuous evaluation of these trends will be necessary.
Sustainability is reshaping surface mount technology (SMT) practices. Companies are now prioritizing eco-friendly materials and processes. This shift reflects a growing commitment to reducing waste and carbon emissions.
Using lead-free solder is one such initiative. It reduces harmful environmental impacts. However, this transition comes with challenges. Manufacturers often face difficulties in achieving consistent quality. Additionally, the alternative materials can be more expensive, forcing companies to rethink their budgets.
Another trend is the adoption of energy-efficient manufacturing methods. Many factories are investing in renewable energy sources like solar and wind. However, these investments require significant upfront costs. Not every company can afford them. The push for sustainability must balance financial viability with environmental responsibility.
| Trend | Description | Impact on SMT Practices | Sustainability Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eco-friendly Materials | Utilizing biodegradable and recyclable materials in SMT components. | Reduces environmental impact and meets regulatory standards. | High |
| Energy-efficient Manufacturing | Adopting practices that lower energy consumption during production. | Decreases operational costs and carbon footprint. | Medium |
| Circular Economy Practices | Implementing systems for reusing and recycling SMT components. | Enhances resource efficiency and reduces waste. | High |
| Smart Manufacturing | Integrating IoT and AI to optimize SMT processes and waste management. | Improves productivity and minimizes material waste. | Medium |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adapting to new regulations on environmental standards. | Ensures legitimacy and market access. | High |

As we look ahead to 2026, the surface mount technology (SMT) industry faces significant growth opportunities. The demand for compact and energy-efficient electronic devices continues to rise. This trend pushes manufacturers to innovate rapidly. However, this innovation isn’t without challenges. The need for advanced materials and skilled labor can complicate production cycles.
Market forecasts suggest robust expansion. Yet, not all regions will benefit equally. For example, developing areas may struggle with infrastructure and training. This creates a gap between capabilities. Sustainability is another pressing issue. The push for greener manufacturing processes is essential. However, implementing these practices can be costly and time-consuming.
Moreover, as technology evolves, supply chain disruptions remain a concern. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global trade. Many companies are still feeling the effects. The ability to adapt quickly is crucial. Investing in local production may mitigate some risks, but it requires upfront investment and careful planning. Balancing growth with sustainable practices will be key to success in the SMT sector moving forward.