-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

Using a Vacuum Reflow Oven can greatly enhance the quality of soldering in electronics manufacturing. This powerful tool provides precise control over temperature and pressure. However, mastering its use requires understanding some critical techniques. Many users overlook simple yet essential steps, leading to potential defects.
First, consider the importance of setting the right temperature profiles. Improper settings can cause issues like solder balls or cold solder joints. Additionally, ensuring the vacuum level is adequate is crucial. A poor vacuum may lead to insufficient soldering results. These elements are vital for achieving consistency in production.
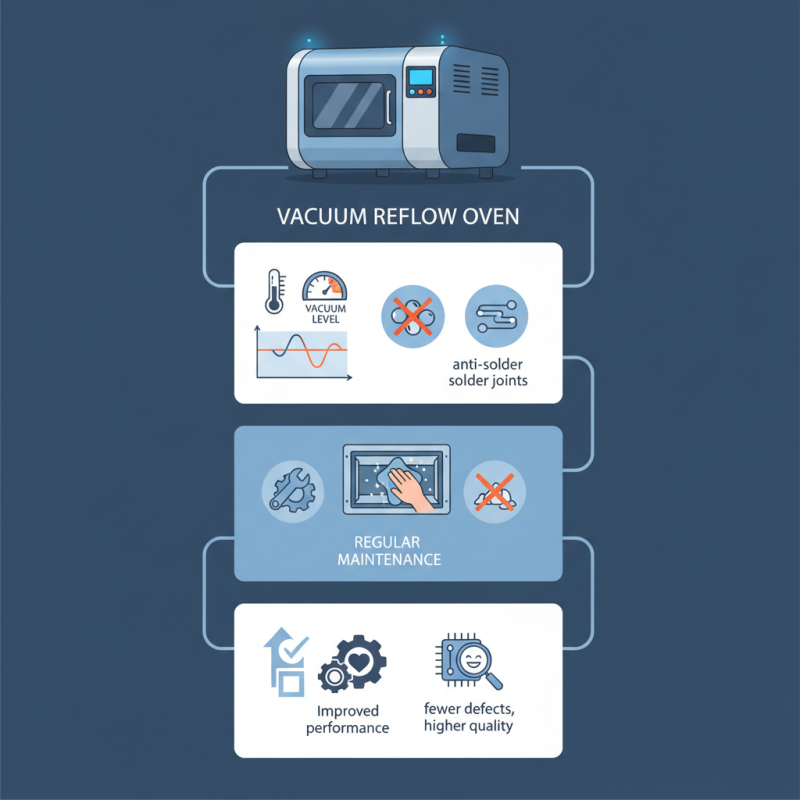
Moreover, regular maintenance of the Vacuum Reflow Oven is often neglected. Without proper care, the oven's performance can decline. Users should regularly check for residues that might affect the process. Over time, these small oversights can accumulate, impacting the overall production quality. Adopting better practices can lead to improved outcomes and fewer reworks.

Vacuum reflow ovens play a crucial role in electronics manufacturing. They provide precise temperature control and atmosphere, significantly impacting soldering quality. Understanding their components is essential for effective use. These ovens typically have a vacuum chamber, heating elements, and a cooling system. Each element needs careful monitoring to ensure optimal performance.
Controlling temperature profiles is key. When mismanaged, these profiles can lead to defects. Poor solder joints or insufficient wetting can occur if the temperature is inconsistent. Additionally, the vacuum level must be adequate. An improper vacuum can lead to air pockets and solder balls. Operators must regularly check the vacuum gauge to prevent these issues.
Another aspect to consider is the PCB layout. Complicated designs may cause uneven heating. It's easy to overlook this, but it significantly affects outcomes. Regularly review and adjust processes for different boards. Ultimately, reflection on these details can enhance the overall soldering process, ensuring higher quality and reliability in the final product.
Using a vacuum reflow oven requires careful planning. One key factor is temperature management. Proper temperature profiles ensure uniform heating. Underheating can lead to poor solder joints. Overheating can damage components. It’s crucial to understand the materials. Different solder types have unique melting points. Knowing these details can prevent mistakes.
Another important aspect is vacuum level. A deeper vacuum often reduces oxidation. This improves solder quality. Monitor the vacuum gauge closely. Fluctuations can indicate problems in sealing. Regular maintenance helps avoid unexpected downtime. It’s vital to check seals and gaskets regularly. Neglecting these components can lead to air leaks.
Finally, consider the board design. Complex designs may require special attention. Large thermal masses can cause uneven heating. Evaluate the layout to ensure efficient heating. Testing with various prototypes is advisable. Learn from any failures along the way. Each reflow process is a chance to improve skills and understanding.
This bar chart illustrates the importance level, on a scale from 1 to 10, of each essential tip for effectively using a vacuum reflow oven. Proper temperature control and thermal profiling are deemed the most critical factors, while maintenance and cleaning procedures are slightly less prioritized.
Preparing materials for a vacuum reflow oven can be a precise process. Start by ensuring your PCB is clean. Any dust or contamination can lead to defects. Use appropriate solvents and lint-free cloths for cleaning. Pay close attention to the surface, as even small residues can affect solderability.
Next, select the right solder paste. The choice of paste impacts the entire reflow process. Keep in mind the paste's viscosity and particle size. Mixing different pastes is not advisable, as it can lead to uneven melting. The again, improper handling can spoil the paste, so always check for expiration dates.
When applying solder paste, use a stencil for accuracy. Misalignment or excessive application can lead to bridging. After application, inspect each PCB closely. Look for any inconsistencies. These small oversights can create bigger issues during the reflow. Engage in regular reflection about your process. Identify what works and what doesn’t. Improvement is a continuous journey in this field.
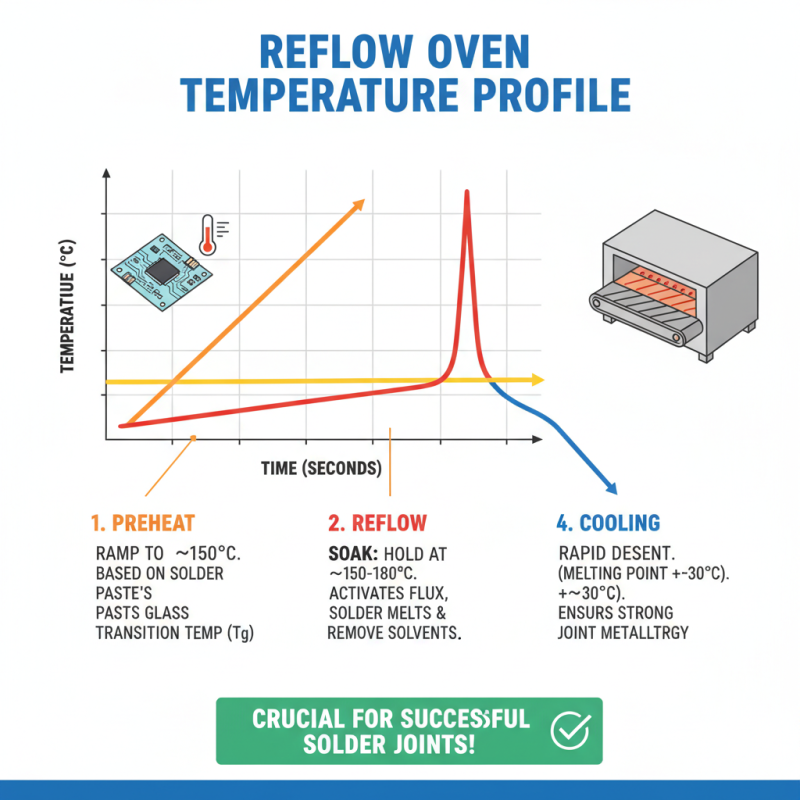
Setting temperature profiles in reflow ovens is crucial for successful soldering. A well-defined profile ensures proper melting and solidification of solder joints. Start by identifying the glass transition temperature of your solder paste. This temperature is essential for determining the preheat segment of the profile.
Gradually ramp up the temperature to avoid thermal shock. The initial phase should be gentle, allowing components to adjust. Too fast of an increase can lead to component failure. Aim for a rate of about 1°C per second during preheat, but feel free to adjust based on your specific materials.
Monitor the peak temperature closely. It should be high enough to melt the solder but not so hot that it damages the components. Many operators overlook the cooling phase, but it’s equally important. An abrupt drop can create thermal stress, leading to cracks or other defects. Be attentive and refine your profile based on real-time feedback. It’s a process of trial and error, requiring continuous adjustments and learning.
Operating a vacuum reflow oven requires attention to detail. One common mistake is not properly preparing the PCB. Make sure to clean the surface before loading it. Residue from previous processes can cause defects. Pay close attention to solder paste application. Uneven distribution can lead to issues during reflow.
Another pitfall is neglecting the importance of temperature profiles. A poorly calibrated profile can result in insufficient heat transfer. It may lead to cold solder joints or overheating components. Regularly check temperature settings and ensure they match the specifications of your materials.
Operators often overlook the importance of vacuum levels. Insufficient vacuum can trap air in the system, causing defects. Ensure the vacuum pump is functioning correctly. Monitor the vacuum gauge for optimal performance. Taking these small steps can significantly improve the outcomes of your reflow process.
| Tip | Description | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Correct Setup | Ensure the oven is properly calibrated before use. | Neglecting calibration, leading to improper heating. |
| Use of Quality Materials | Select high-quality solder paste compatible with your components. | Using incorrect or poor-quality materials can cause defects. |
| Proper Vacuum Control | Maintain consistent vacuum levels throughout the process. | Fluctuating vacuum levels can lead to soldering issues. |
| Monitor Temperature Profiles | Utilize reliable temperature profiling for optimal results. | Ignoring temperature profiles can result in component damage. |
| Solder Paste Application | Apply solder paste uniformly to avoid shorts and opens. | Inconsistent paste application can result in poor connections. |
| Component Placement | Accurately place components to prevent misalignment. | Misplacing components can hinder soldering effectiveness. |
| Regular Maintenance | Perform routine checks and maintenance on the oven. | Neglecting maintenance can lead to operational failures. |
| Cooling Procedure | Allow components to cool properly post-reflow. | Rapid cooling can cause thermal stress and warping. |
| Documentation | Keep detailed records of settings and outcomes. | Inconsistent documentation can lead to repeated errors. |
| Training | Ensure operators are well-trained in oven operation. | Lack of training can result in misuse and mishaps. |