-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

In the world of electronics manufacturing, achieving flawless connections between components is essential for device functionality and longevity. One highly effective method for ensuring these connections is through SMT reflow soldering. This technique allows for the precise application of soldering materials to surface-mounted devices, creating reliable electrical connections with minimal damage to sensitive components. As technology continues to advance, mastering SMT reflow soldering techniques becomes increasingly important for engineers and hobbyists alike.
This guide will explore fundamental concepts and advanced practices related to SMT reflow soldering, equipping you with the knowledge to perfect your soldering skills. Whether you are a beginner looking to understand the basics or an experienced technician seeking to refine your approach, mastering these techniques will enhance your capability to create robust and efficient electronic assemblies. By the end of this exploration, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to optimize your SMT reflow soldering processes, ensuring high-quality results every time.
Surface mount technology (SMT) reflow soldering is an essential technique in modern electronics manufacturing. This process involves the melting of solder paste to create strong electrical connections between surface-mounted components and printed circuit boards (PCBs). According to a report by IHS Markit, the global SMT market is expected to reach $33.5 billion by 2025, emphasizing the growing importance of efficient soldering techniques in the industry. Mastering these techniques not only enhances the reliability of connections but also significantly reduces production costs and increases throughput.
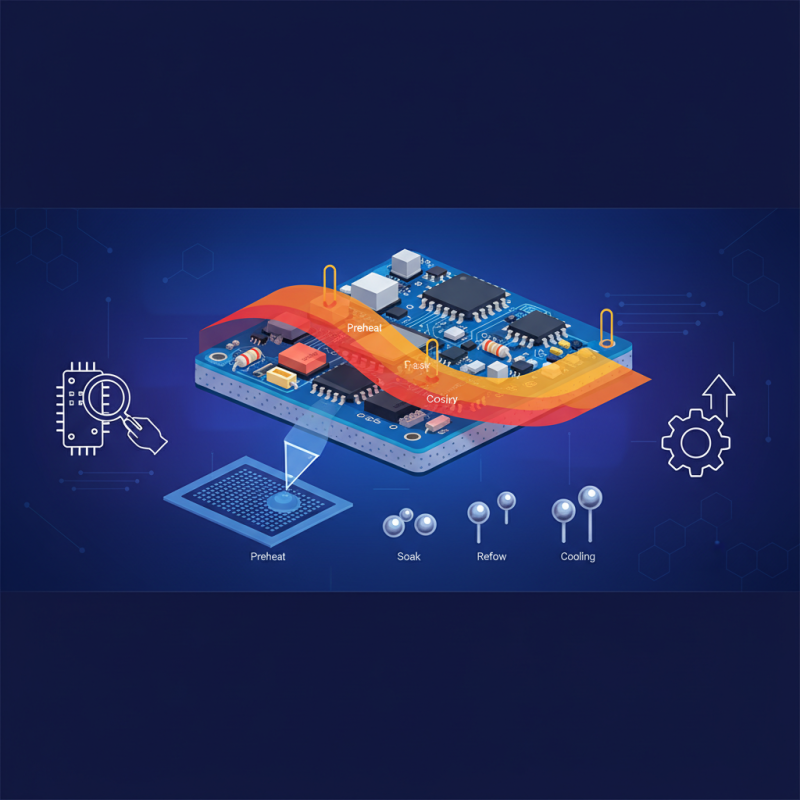
One key principle of SMT reflow soldering is thermal profiling. Proper thermal management during the reflow process ensures that all components achieve the necessary temperature to melt the solder without damaging sensitive components. A study from IPC—Association Connecting Electronics Industries indicates that nearly 70% of soldering defects arise from inadequate thermal profiles. Therefore, investing in advanced thermal profiling equipment can yield substantial improvements in solder joint quality.
Tips: To achieve optimal results in SMT reflow soldering, it is crucial to use high-quality solder paste and maintain a clean PCB. Regularly calibrate your reflow oven to ensure consistent temperature settings, and consider using a thermal camera to monitor temperature distribution. Finally, perform routine inspections of solder joints to catch potential defects early in the production process.
When embarking on SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow soldering, having the right tools and equipment is paramount to achieving flawless solder joints. The core essentials include a high-quality reflow oven, solder paste, stencils, and a reliable pick-and-place machine. A reflow oven provides precise temperature control crucial for melting the solder paste and ensuring optimal connections between the components and the PCB. It's important to choose an oven that allows for consistent thermal profiles to accommodate various components and board designs.
In addition to these primary tools, an accurate temperature probe is necessary for monitoring thermal conditions during the reflow process. Stencils cut to match the pad layout are crucial for applying an even layer of solder paste, ensuring that each component receives the right amount of solder for a robust connection. Additionally, a good quality pick-and-place machine speeds up the assembly process while maintaining accuracy in component placement. Together, these tools create a comprehensive setup that significantly enhances the quality and reliability of SMT soldering operations. Proper maintenance of these tools is equally important, as it ensures their longevity and consistent performance.

Mastering SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow soldering techniques is essential for achieving reliable and high-quality connections in electronic circuit assemblies. The process begins with proper preparation, which involves ensuring that the printed circuit board (PCB) is clean and free of contaminants. Once the PCB is ready, the next step is to apply solder paste to the designated pads. This can be done using a stencil, which helps in applying the right amount of solder paste precisely where it's needed, minimizing wastage and ensuring consistent results.
After the solder paste application, the placement of surface mount components follows. Using a pick and place machine or manual techniques, components must be aligned accurately with the solder paste. Care must be taken to avoid misalignment, as this can lead to improper solder joints. The next critical step is the reflow process, where the assembled board is heated in a reflow oven. The temperature profile must be carefully controlled to allow the solder paste to melt and form strong solder joints as it cools. Monitoring the temperature and time during this phase is crucial to avoid thermal shock or poor solder connections, ultimately leading to a flawless finish and optimal functionality of the electronics.
Smt reflow soldering is a critical technique in electronics manufacturing, but it presents a variety of challenges that can impact the quality of connections. One common issue is inadequate solder joint formation, often due to improper temperature profiles during the reflow process. It is essential to accurately calibrate heat zones to ensure that components reach the desired melting temperature for solder paste without overheating sensitive parts. A well-optimized profile usually includes preheating, soaking, and reflow stages, which must be carefully adjusted based on the specifics of the solder alloy and PCB materials used.
Another challenge involves managing the placement and alignment of surface-mount components. Misalignment can lead to poor electrical connections and may even cause parts to fall off the board during processing. Utilizing pick-and-place equipment equipped with precise vision systems can greatly reduce placement errors. Additionally, implementing thorough inspection protocols, such as automated optical inspection (AOI), helps quickly identify issues before further assembly. By addressing these common challenges with systematic approaches, manufacturers can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of soldered connections in their electronic products.
Achieving reliable connections in SMT reflow soldering requires attention to several best practices that can significantly impact the quality and durability of electronic assemblies. First and foremost, proper surface preparation is crucial; this includes ensuring that both the PCB and the components are free from contaminants such as dust, grease, or oxidation. A clean surface guarantees better wetting and adhesion of the solder, which ultimately leads to stronger joints. Additionally, selecting the appropriate solder paste is essential, as it should match the components’ specifications and the reflow profile of the PCB.
Furthermore, optimizing the reflow profile plays a vital role in the soldering process. This involves carefully controlling the temperature ramp, soaking time, and cooling rate during reflow. A well-optimized profile ensures that the solder paste melts at the right temperature and forms reliable connections without causing thermal shock to sensitive components. Monitoring the atmosphere in the reflow oven is also important, as it helps prevent oxidation and improves solder flow. Regular calibration and maintenance of equipment can contribute to achieving consistent and high-quality solder joints, which are the backbone of any reliable electronic assembly.