-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

In the intricate world of electronics manufacturing, mastering Smt Reflow Soldering is essential for achieving high-quality results and longevity in products. As experts in the field continue to emphasize the importance of precision and technique, renowned engineer Dr. Emily Chen states, “The key to flawless Smt Reflow Soldering lies in understanding the thermal dynamics of the process.” This highlights the significance of employing the right methods to ensure that components are securely and efficiently attached to the circuit boards.
Smt Reflow Soldering is not just a technical requirement; it is an art that combines science with skill. The nuances involved in temperature regulation, solder paste application, and the choice of proper profiles can dramatically influence the performance and reliability of electronic assemblies. By honing one’s technique, operators can minimize defects, enhance yield, and streamline production workflows.
As we delve deeper into the various aspects of Smt Reflow Soldering, it becomes apparent that mastery in this field is achievable through continual learning and practice. This guide aims to provide you with valuable tips and insights to refine your technique and elevate your soldering skills to the next level.

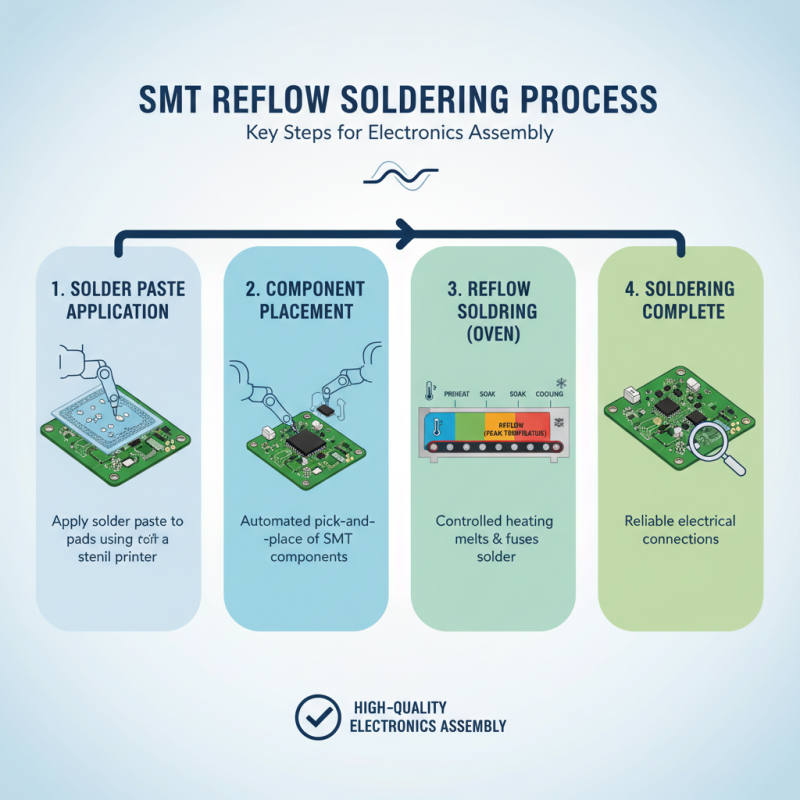
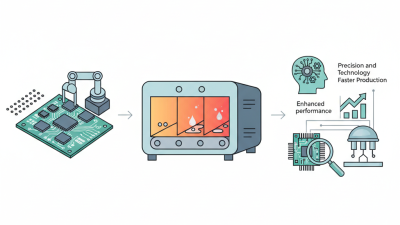
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow soldering is a critical process in modern electronics manufacturing, allowing for the efficient and reliable assembly of components on circuit boards. Understanding the key concepts behind SMT reflow soldering is essential for achieving high-quality results. The process involves applying solder paste to a PCB, placing SMT components, and subjecting the assembly to controlled heating in a reflow oven. This heating process melts the solder paste, allowing it to flow and create strong electrical connections once cooled.
The importance of mastering SMT reflow soldering cannot be overstated, as it directly affects the performance and longevity of electronic devices. A well-executed soldering process minimizes defects such as cold solder joints and bridging, which can lead to circuit failure. Moreover, in an increasingly compact world of electronics, mastering SMT techniques can facilitate the assembly of smaller, more intricate devices without sacrificing reliability. Understanding thermal profiles, the physics of solder paste behavior, and the characteristics of various components is crucial in refining your technique and ensuring successful applications in complex electronic systems.
When it comes to SMT reflow soldering, having the right tools is essential for achieving high-quality results. The core equipment includes a reliable reflow oven, which is crucial for evenly heating the solder and ensuring a strong bond between the components and the PCB. Additionally, a good solder paste stencil is necessary for precise application of solder paste on the pads, helping to prevent defects during the soldering process.
Incorporating proper handling tools, such as tweezers and vacuum pick-ups, can enhance your workflow. These tools allow for better placement of small components, reducing the risk of misalignment. A hot air rework station can also come in handy for re-soldering or fixing mistakes after the reflow process, providing flexibility and precision.
When mastering SMT reflow soldering, remember to keep your workspace organized. A clean and well-structured area can help you avoid mistakes and streamline your workflow. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the reflow profile settings of your equipment, as proper temperature settings are critical in ensuring the optimal melting and solidification of solder paste. By honing these skills and maintaining the necessary equipment, you can perfect your SMT reflow soldering technique.
Temperature profiles are critical in achieving optimal results in reflow soldering, as they directly influence the quality of the solder joints and the overall reliability of the electronic assembly. A well-defined temperature profile consists of several stages, including preheating, soaking, reflow, and cooling. Each of these stages plays a unique role in ensuring that the solder paste effectively melts and forms a solid connection between the components and the PCB. Proper control of the heating rate, peak temperature, and cooling rate is essential to avoid issues such as insufficient solder wetting, tombstoning, and thermal shock.
Best practices for creating effective temperature profiles involve careful calibration of the reflow oven and close monitoring of the process. Utilizing thermocouples to measure temperatures at critical points on the PCB allows for real-time adjustments to be made to the oven settings. Additionally, conducting experiments with different temperature profiles can help identify the optimal conditions for specific solder materials and component types. The goal is to establish a profile that minimizes thermal stress while ensuring that the solder reaches its ideal melting point, allowing for proper flow and adherence. By consistently applying these techniques, practitioners can enhance the reliability and performance of their soldered connections, leading to improved product quality.
This chart illustrates the optimal temperature profiles used in reflow soldering, helping you understand the significance of each phase in the process.
Reflow soldering is an essential process in electronics manufacturing, yet it is prone to several common defects that can significantly affect the performance and reliability of solder joints. Identification of these defects, such as solder bridges, cold joints, and voids, is critical for maintaining quality. According to a recent industry report by IPC, around 60% of solder-related failures in electronic assemblies are attributed to poor reflow techniques. This statistic underscores the importance of mastering proper techniques to prevent such defects effectively.
To prevent solder bridges, one of the most frequent issues in reflow soldering, it is crucial to optimize the pad size and spacing on the PCB. Ensuring that the stencil apertures are correctly designed can also mitigate excessive solder application. Additionally, monitoring the reflow temperature profile is vital in preventing cold joints, which occur when the solder does not fully melt or flows inadequately. IPC research indicates that an appropriate peak temperature and dwell time can reduce cold joint instances significantly.
Tips for improving reflow soldering include regularly calibrating your reflow oven to ensure precise temperature control and using high-quality solder paste to enhance wetting properties. Moreover, implementing proper cleaning procedures for PCBs before soldering can help minimize oxidation, thus improving solder joint integrity. By focusing on these strategies, manufacturers can enhance production efficiency and reduce the likelihood of defects in their electronic assemblies.
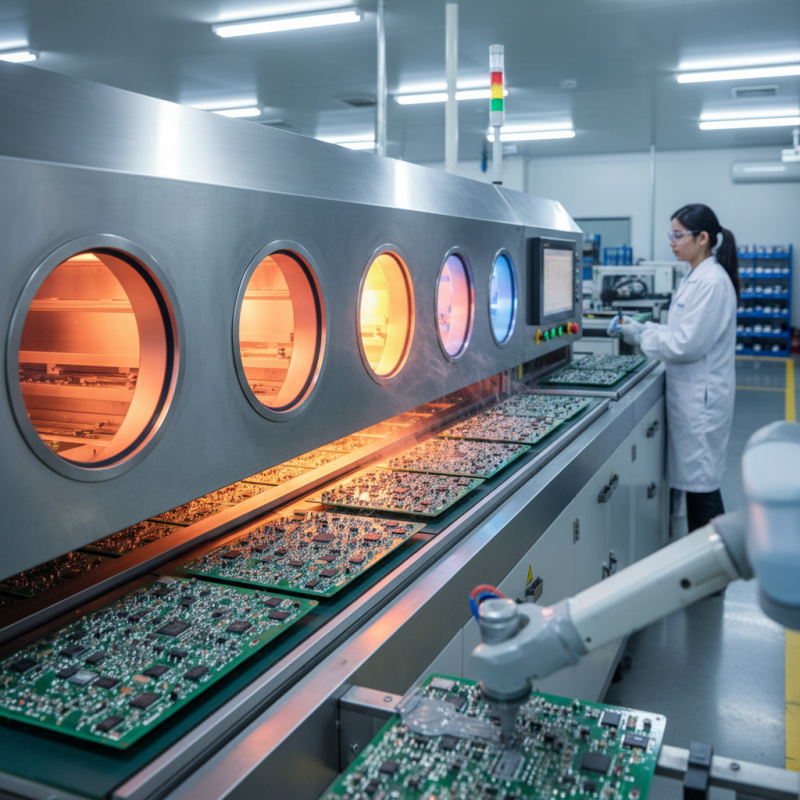
In the realm of SMT reflow soldering, testing and quality assurance are crucial components that ensure the reliability and effectiveness of electronic assemblies. Adhering to industry standards is essential for maintaining high-quality production processes. One widely recognized standard is IPC-A-610, which outlines the acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies. By following these guidelines, manufacturers can ensure that solder joints meet performance specifications and that components are securely attached to the PCB.
Furthermore, implementing rigorous testing procedures at various stages of the manufacturing process can help identify defects early and reduce the risk of product failures. Techniques such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection are vital in detecting issues like insufficient solder, misaligned components, and other anomalies that may affect performance. By incorporating these quality assurance measures, manufacturers can not only comply with industry standards but also improve overall production efficiency and customer satisfaction, leading to a more robust and reliable end product.