-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

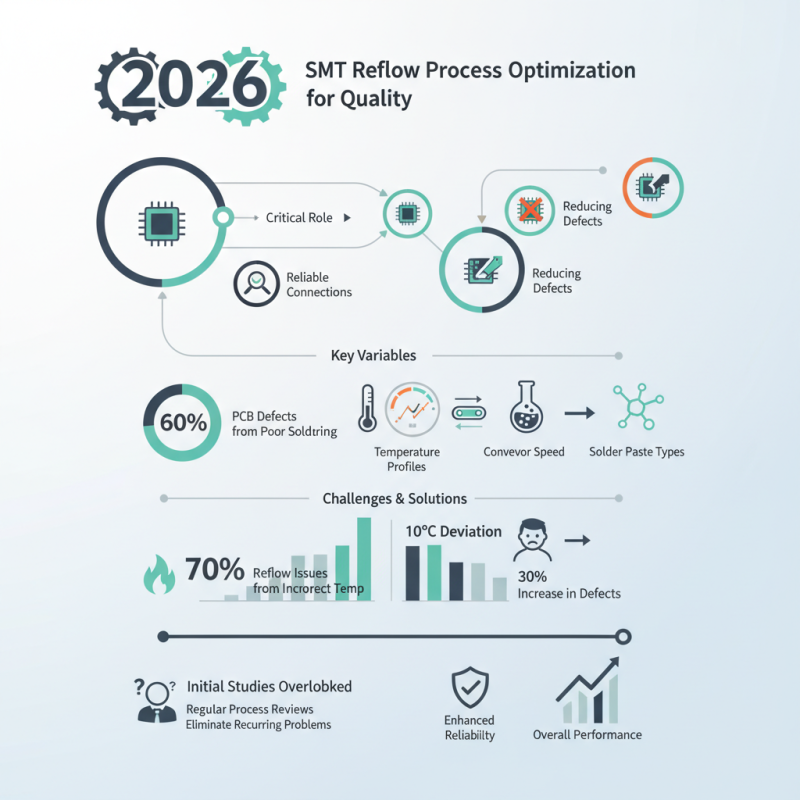
The SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow process plays a critical role in electronic manufacturing. A high-quality SMT reflow process ensures reliable connections, reducing defects in PCB assemblies. According to IPC-610 standards, over 60% of PCB defects arise from poor soldering practices. This underscores the importance of optimizing the SMT reflow process for better outcomes.
To achieve better quality results in SMT reflow, understanding variables such as temperature profiles, conveyor speed, and solder paste types is crucial. Studies suggest that 70% of reflow issues stem from incorrect temperature settings. Industry reports indicate that a 10°C deviation in peak temperature can result in a 30% increase in defects.
Many companies still face challenges in perfecting their reflow parameters. Some overlook the importance of initial studies and adjustments. Regular process reviews can provide insights that help eliminate recurring problems. Industry leaders often highlight the need for continuous improvement. By refining the SMT reflow process, manufacturers can enhance product reliability and overall performance in a competitive market.
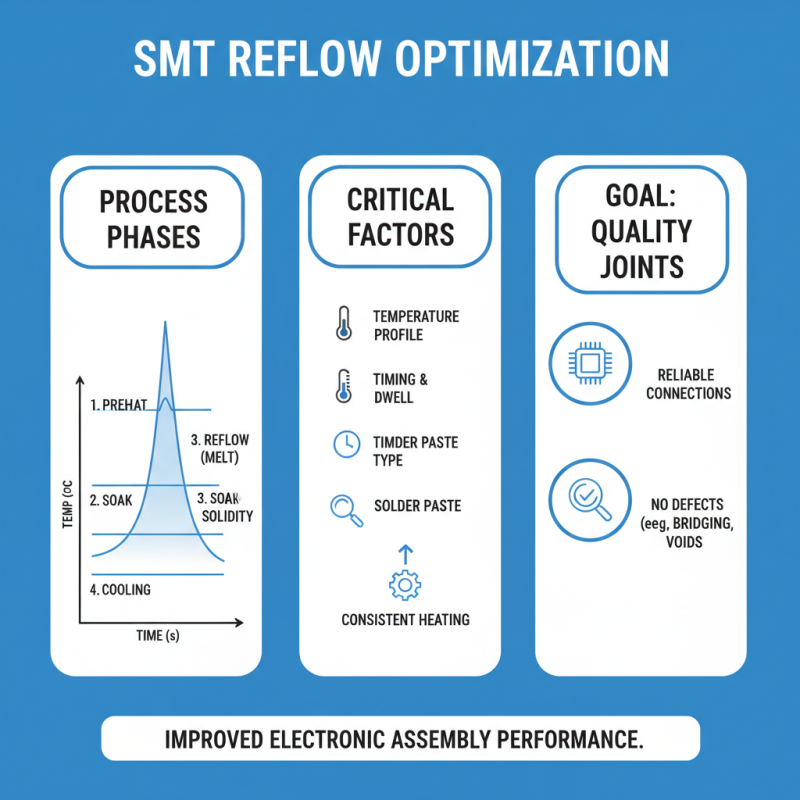
Optimizing the SMT reflow process is crucial for achieving high-quality solder joints and overall performance in electronic assemblies. The reflow process involves heating, melting solder paste, and allowing it to solidify to create reliable connections. To truly understand this process, one must pay attention to various factors. Temperature profiles, for instance, can be tricky. An ideal curve has multiple phases, but it’s easy to misjudge timing.
Cooling rates also play a significant role. Too fast cooling can lead to thermal shock, while too slow may cause defects. Both extremes can lead to unreliable solder joints. There are no perfect practices, and constant monitoring is essential. You might find some boards with well-defined profiles struggle to meet quality standards. The transition from peak to cooling must be smooth to avoid inconsistencies.
Designing an effective layout with adequate solder paste application is equally important. Irregularities in paste deposition can cause issues during reflow, like insufficient bonding or cold joints. Using automated methods helps, but imperfections can happen. Regular reviews and adjustments based on real-time feedback can lead to improvements. Understanding these aspects is vital for refining the SMT reflow process and ensuring better quality results.
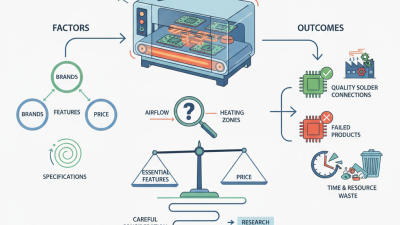
The quality of the SMT reflow process is influenced by several key factors. One important aspect is temperature profiling. Studies show that improper temperature profiles can lead to issues like solder balling and insufficient wetting. Effective profiling can increase the likelihood of consistent solder joints, with reports suggesting an optimal peak temperature range between 235°C to 250°C.
Another significant factor is the choice of solder paste. Different pastes exhibit varying characteristics, impacting their melting point and viscosity. Selecting the right paste affects the reflow process's success. However, many companies often overlook the importance of matching the paste to the specific PCB assembly requirements. Inadequate paste application can lead to defects, with studies indicating that up to 30% of solder joints can fail due to paste-related issues.
Stencil design plays a crucial role as well. A poorly designed stencil can result in inconsistent solder deposits. This inconsistency can compromise the integrity of connections, leading to potential failures down the line. Recent analyses highlight that optimizing stencil thickness and aperture shapes can enhance solder volume control. While these factors are essential, continuous monitoring and adjustment remain imperative for achieving high-quality reflow results.
Optimizing the SMT reflow process is essential for achieving high-quality results. Setting the right reflow oven profiles plays a crucial role. Start by establishing a well-defined temperature profile. This considers the preheat, soak, reflow, and cooling phases. Each stage needs precise timing and temperature settings.
When developing your profile, monitor the temperature at multiple points inside the oven. This data will help identify hot or cold spots that could affect solder joint quality. Regular calibration of the thermal profiling tools is necessary. Any discrepancies can lead to poor solderability and unreliable connections.
**Tips:** Adjust the conveyor speed to ensure proper exposure time at each stage. This varies with different PCB types and component densities. Sometimes, you may notice excessive solder beads or cold solder joints. Review your profiles often. Reflect on the changes made and their impacts on production efficiency. It’s vital to document any adjustments and their outcomes thoroughly. Experimentation and reflection can lead to better results.
In the SMT reflow process, various challenges can affect the final quality of products. One common issue is temperature inconsistency. Uneven heating can lead to poor solder joints. This problem typically arises from an improperly calibrated oven. Ensuring that temperature zones are balanced is crucial for minimizing this risk. Regular checks and adjustments can help maintain adequate heating.
Another significant challenge is solder paste application. If the paste is either too thick or too thin, it can adversely affect adhesion. Inconsistent printing leads to voids or insufficient solder. Using appropriate stencil designs can help improve paste transfer. Additionally, operators need proper training to achieve optimal paste application.
Monitoring and controlling the cooling phase is also essential. Rapid cooling can create mechanical stress on solder joints. This stress may lead to cracks over time. A controlled cooling rate allows for better joint integrity. Overall, addressing these challenges requires continuous improvements and reflections on current processes.
In the realm of SMT reflow processes, continuous monitoring is crucial. An effective way to start is by tracking temperature profiles meticulously. Each PCB may behave differently under heat. Small variances in temperature can affect solder quality. Regularly calibrating your thermal sensors ensures accuracy over time.
Combining real-time data with actionable insights can enhance quality. Using automated systems can flag anomalies instantly. However, relying solely on automation may overlook subtle issues. Human oversight is essential; operators should analyze patterns and trends. Reflecting on past errors allows teams to implement better practices.
Furthermore, training staff regularly is vital. Knowledge can fade, and skills can diminish without practice. A well-informed team will adapt to changes and optimize processes. Engaging everyone in quality discussions fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Creating feedback loops enables teams to evolve based on experiences and results. Remember, perfection is an ongoing journey, not a destination.