-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

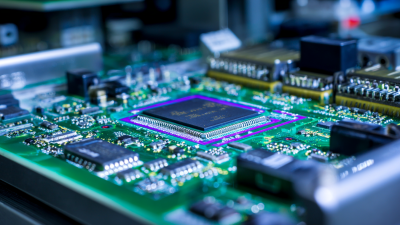
In the intricate world of electronics assembly, Smt Reflow Soldering stands out as a pivotal technique that ensures the reliability and efficiency of electronic components. This process involves the melting of solder paste to create permanent connections on printed circuit boards (PCBs), facilitating the integration of various electronic parts. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a noted expert in the field of electronics manufacturing, "Smt Reflow Soldering is not just a method, but a crucial art that combines precision and technology to enhance the performance of modern electronics."
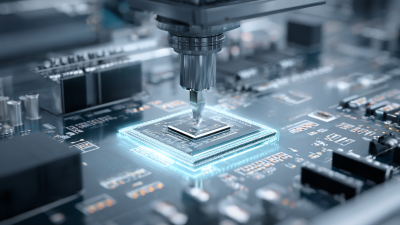
Understanding how Smt Reflow Soldering works is essential for manufacturers seeking to optimize their production processes. The reflow process relies on precisely controlled heat profiles to melt solder paste, allowing it to flow and bond between component leads and the PCB pads. As the industry continues to evolve, the techniques and technologies surrounding Smt Reflow Soldering are also advancing, enabling faster production times and improved product reliability.
As electronic devices become increasingly complex, mastering Smt Reflow Soldering is vital for ensuring quality and functionality. This process not only underscores the importance of proper assembly techniques but also highlights the continuous pursuit of innovation within the electronics manufacturing sector. With experts like Dr. Carter at the forefront, the future of Smt Reflow Soldering promises to remain bright and impactful in shaping the electronic landscape.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) reflow soldering is a critical process in electronics assembly. This technique involves the soldering of electronic components to printed circuit boards (PCBs) by melting solder paste, which consists of small solder balls mixed with flux. The process typically consists of several stages: solder paste application, component placement, reflow, and cooling. According to the IPC-A-610 standards, the quality of solder joints achieved through proper reflow techniques can significantly influence the reliability of the final product.
The reflow soldering process typically employs temperature profiles that reflect thermal characteristics of both the solder and the components. The melting point of lead-free solders usually ranges from 217°C to 227°C. Advanced reflow ovens use sophisticated control systems to ensure optimal temperature gradients, which have been shown to enhance joint strength and reduce defects, such as cold joints and tombstoning. Reports from the IPC indicate that effective reflow soldering can lead to a reduction in assembly defects by 30% or more, which is vital for maintaining high manufacturing standards in the electronics industry.
In the context of growing demand for compact and efficient electronic devices, SMT reflow soldering continues to dominate the market due to its ability to support high-density components with minimal footprint. A report from Research and Markets projects that the global SMT soldering market will reach USD 6.5 billion by 2026, driven by innovations in assembly technologies and the increasing complexity of electronic products. This underscores the importance of mastering SMT reflow soldering techniques to ensure effective production processes in modern electronics assembly.
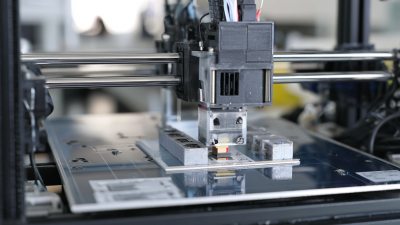
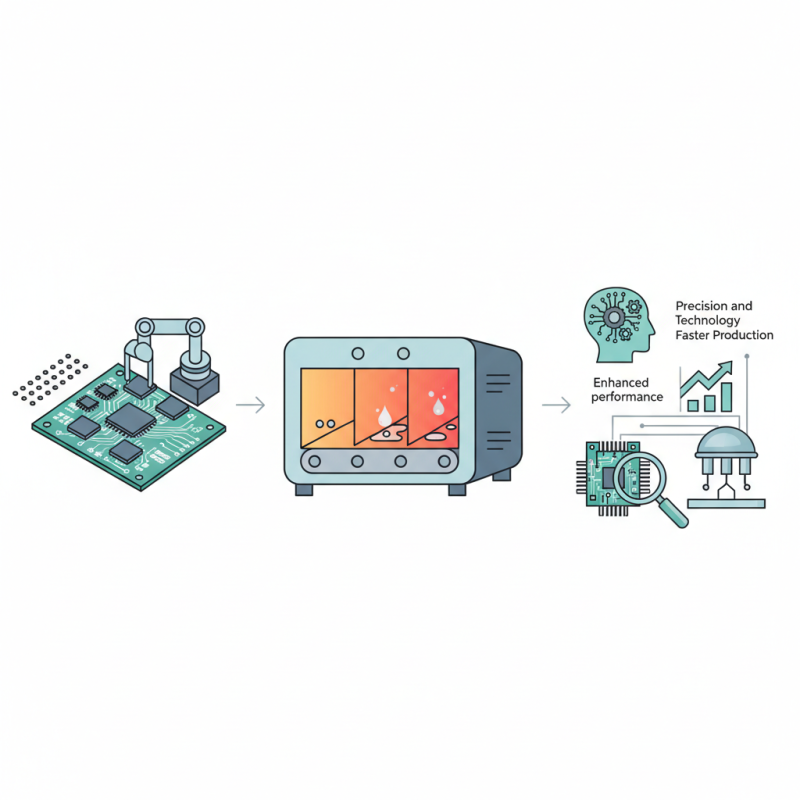
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow soldering is a crucial process in electronics assembly that ensures the reliable connection of components to printed circuit boards (PCBs). The reflow soldering process comprises several steps that facilitate the effective formation of solder joints. First, a solder paste composed of tiny metal spheres and flux is applied to the PCB using a stencil. This paste serves as the adhesive medium for component placement.
Next, surface mount components are precisely positioned on the paste using automated pick-and-place machines.
Once the components are secured, the PCB enters a reflow oven where it undergoes temperature cycling. The oven typically features multiple heating zones, gradually raising the temperature to a peak soldering temperature between 240-250 degrees Celsius. This process causes the solder to melt and flow, creating strong and reliable solder joints. According to industry reports, the reflow soldering process accounts for over 80% of all soldering operations in modern electronic assembly due to its efficiency and scalability.
Tips: Ensure proper stencil design to minimize solder paste defects. Regular maintenance of the pick-and-place machine can also enhance placement accuracy, reducing rework and improving overall yield in the assembly process. In addition, careful monitoring of the reflow profile is essential to avoid solder bridging and other defects, ensuring the highest quality in your electronic assemblies.
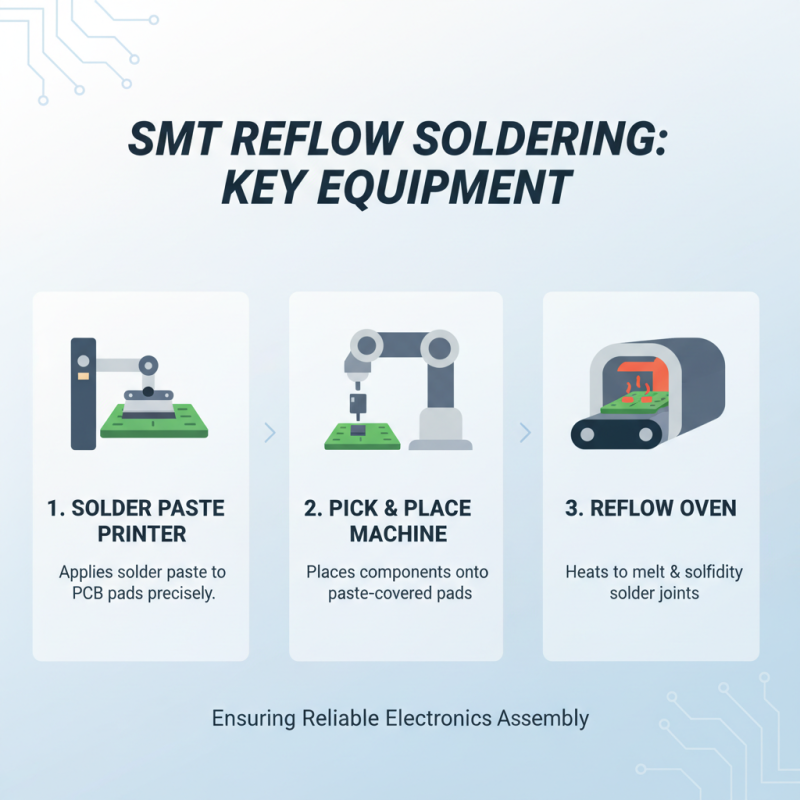
In SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow soldering, several key pieces of equipment and tools play a crucial role in ensuring effective and reliable solder joint formation during electronics assembly. One of the primary components is the solder paste printer, which applies solder paste onto the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) pads with precision. This process is vital, as the quality of the solder paste application directly affects the soldering process, influencing factors such as the amount and distribution of solder for each joint.
Another essential piece of equipment is the reflow oven, which heats the PCB and solder paste to melt the solder and create a solid electrical connection between the components and the board. Reflow ovens come in various designs, such as conveyor-type models that ensure consistent temperature profiles, allowing for uniform heating and cooling cycles. Additionally, a pick-and-place machine is crucial in automating the assembly process, positioning surface-mounted components on the solder paste correctly before the reflow process begins. Together, these tools streamline the SMT reflow soldering process, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in electronics manufacturing.

The quality of SMT reflow soldering is critically influenced by several parameters that must be carefully controlled throughout the assembly process. One of the most significant factors is the temperature profile during the reflow process. This profile must be optimized to ensure proper solder melting and solidification, which is essential for creating reliable electrical connections. Variations in peak temperature and the rate of heating and cooling can lead to defects such as insufficient wetting, solder bridging, and even damage to sensitive components.
Another key parameter is the solder paste application. The thickness, uniformity, and volume of solder paste directly affect solder joint quality. Insufficient paste can result in cold solder joints, while excessive paste can lead to solder bridging and other issues. Therefore, employing precise printing techniques and ensuring that the parameters used in the stencil printing process are correctly set are essential for achieving optimal results.
**Tips:** Always conduct thorough testing of your reflow oven's temperature settings and regularly maintain equipment to avoid fluctuations that could compromise solder quality. Additionally, consider experimenting with different solder paste formulations to identify the best fit for your specific components and assembly requirements. Regular inspections can catch potential issues before they escalate, ensuring a smoother production process.
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reflow soldering is crucial in the electronics assembly industry, enabling the efficient and reliable soldering of surface mount components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Adhering to industry standards like IPC-A-610 ensures that all soldering processes meet quality and reliability expectations. This standard provides guidelines on acceptable solder joint quality and defines the criteria for various classes of assemblies, helping manufacturers maintain consistency in production. According to a report from IPC, the global electronics manufacturing market is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2025, underlining the importance of sound soldering practices in meeting the increasing demand for electronic devices.
Best practices for SMT reflow soldering include meticulous control of temperature profiles during the reflow process to optimize solder melt quality. Profiles should be customized depending on the type of solder paste and components used to prevent issues such as cold solder joints or component damage from overheating. A study by the National Electronics Manufacturing Initiative reveals that implementing advanced reflow oven technologies can increase yield rates by up to 30%, highlighting the impact of precise thermal management. Furthermore, regular training for assembly personnel on these best practices is vital to ensure adherence to standards, minimize defects, and enhance overall product reliability.