-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

Smt Reflow Soldering is a critical process in electronics manufacturing that ensures the reliable and efficient assembly of electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). According to Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned expert in electronics manufacturing, "The precision of Smt Reflow Soldering not only enhances the performance of the final products but also significantly reduces manufacturing defects." The process involves applying solder paste to the PCB, placing components, and then heating the assembly to melt the solder for secure connections.
As technology continues to advance and components become more compact, the importance of Smt Reflow Soldering cannot be overstated. It allows for high-density assembly and is essential for producing modern electronic devices that require speed and accuracy. The controlled heating and cooling cycles of the reflow process ensure a strong bond between components, playing a key role in the overall durability and functionality of electronic products. Understanding Smt Reflow Soldering is fundamental for industry professionals aiming to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing.

Surface Mount Technology (SMT) reflow soldering is a pivotal process in electronics manufacturing, enabling the precise assembly of components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). This method involves several key steps, starting with the application of solder paste to the PCB, which is typically done using a stencil. Solder paste is a mixture of tiny solder balls and flux that helps facilitate the soldering process. Once the paste is in place, surface mount components are strategically positioned on the PCB’s pads.
The assembly then undergoes a reflow process, where the board is heated in a reflow oven. This oven uses a carefully controlled heating profile to raise the temperature of the PCB and the components gradually. As the temperature increases, the solder paste melts and forms a reliable electrical and mechanical connection between the component leads and the PCB pads. After reaching the peak temperature, the board is cooled down, solidifying the solder. This method not only enhances manufacturing efficiency but also ensures the robustness and reliability of electronic devices by providing strong solder joints that can withstand thermal and mechanical stress in varied operating environments.
The SMT reflow soldering process is a critical step in electronics manufacturing, involving several key components that work together to ensure a reliable solder joint between electronic components and the printed circuit board (PCB). At the heart of this process is the reflow oven, which utilizes a temperature profile to melt the solder paste that has been applied to the PCB. This profile includes precise heating stages: preheating, soaking, reflow, and cooling, each designed to optimize the soldering process and minimize thermal stress on sensitive components.
Another essential component is the solder paste itself, which is a mixture of tiny solder spheres and a flux. The application of solder paste is typically performed using a stencil printer, ensuring that the right amount is deposited on the designated pads of the PCB. The flux plays a crucial role in cleaning the surfaces and preventing oxidation, enabling better wetting of the solder. Additionally, the selection of appropriate PCB materials and components is vital, as they must withstand the thermal cycles without damage. Together, these elements contribute to the effectiveness and efficiency of the SMT reflow soldering process in producing high-quality electronic products.
The SMT reflow soldering process is a critical method used in electronics manufacturing, involving several key steps to ensure reliable connections between electronic components and circuit boards. Initially, the process begins with the application of solder paste onto the printed circuit board (PCB) using a stencil. This paste consists of tiny solder balls mixed with flux, which helps promote better adhesion during soldering. The precise placement of solder paste is crucial, as it determines the quality and effectiveness of the solder joints after reflow.
Once the solder paste is applied, electronic components are then placed onto the PCB using automated pick-and-place machines. These machines accurately position each component over the solder paste-covered pads. After placement, the board is subjected to a heating process in a reflow oven. The oven gradually increases the temperature, causing the solder paste to melt and form joints between the components and the PCB.
The temperature profile is meticulously controlled to ensure that the solder melts and then solidifies uniformly, creating strong connections. This intricate process ultimately guarantees optimal performance and longevity of electronic devices.
SMT reflow soldering plays a crucial role in electronics manufacturing, offering numerous advantages that enhance production efficiency and product reliability. One of the primary benefits of this soldering technique is its ability to create strong, consistent solder joints by melting solder paste in a controlled oven environment. According to a recent report by IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits), the use of reflow soldering has led to a reduction in solder joint defects by approximately 30%, making it a preferred choice for assembling complex printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Another key advantage of SMT reflow soldering is its capacity for high-volume production. Automated processes can handle multiple PCBs simultaneously, significantly increasing throughput. Industry analysis from market research firm Research and Markets estimates that the global SMT assembly market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6% from 2023 to 2028, driven largely by the scalability and efficiency of reflow soldering techniques. This ensures that manufacturers can meet rising demands while maintaining quality standards. Furthermore, the reduction in manual handling during the soldering process minimizes the risk of human error, further enhancing assembly reliability in today's fast-paced electronics environment.
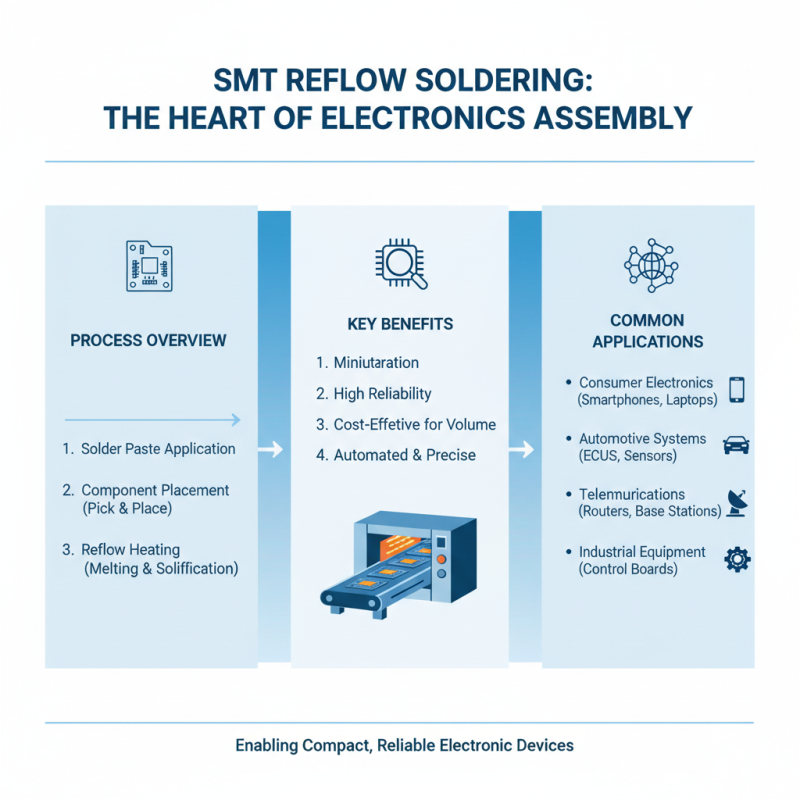
SMT reflow soldering plays a pivotal role in the electronics manufacturing industry, particularly in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process is essential for creating reliable and compact electronic devices. Common applications of SMT reflow soldering include consumer electronics, automotive systems, telecommunications, and industrial equipment. In consumer electronics, this technique is utilized to assemble devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, where miniaturization and efficiency are critical. The ability to place numerous components on a small PCB while maintaining high reliability makes SMT reflow soldering an invaluable process.
In the automotive sector, SMT reflow soldering is employed for the assembly of various components, including sensors, control modules, and infotainment systems. These components must withstand rigorous testing and harsh environments, highlighting the importance of the robust connections formed through reflow soldering. Additionally, in telecommunications, this method is essential for the manufacturing of infrastructure equipment like routers and switches, where fast signaling and performance reliability are crucial. Overall, SMT reflow soldering facilitates the complex manufacturing processes needed across a diverse range of industries, ensuring the functionality and durability of modern electronic devices.