-
Home
-
Products
-
News
-
About Us
-
Support center
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
inquiry
Leave Your Message

A Solder Reflow Oven is essential in electronics manufacturing. It plays a crucial role in soldering components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). According to a market research report by Grand View Research, the global reflow oven market is expected to reach $1.4 billion by 2025, reflecting significant growth in the electronics industry.
These ovens operate by heating solder paste on PCBs to create strong electrical connections. Typically, they utilize a conveyor system to move boards through various temperature zones. The process requires precision to avoid defects such as insufficient solder or overheating. However, achieving this level of control can be challenging, particularly for small-scale operations.
As production demands increase, manufacturers must continually adapt their techniques. Some may overlook the importance of routine maintenance, affecting oven performance over time. As the technology advances, it poses questions about sustainability and resource use. Balancing efficiency with environmental responsibility remains a critical conversation in the industry.
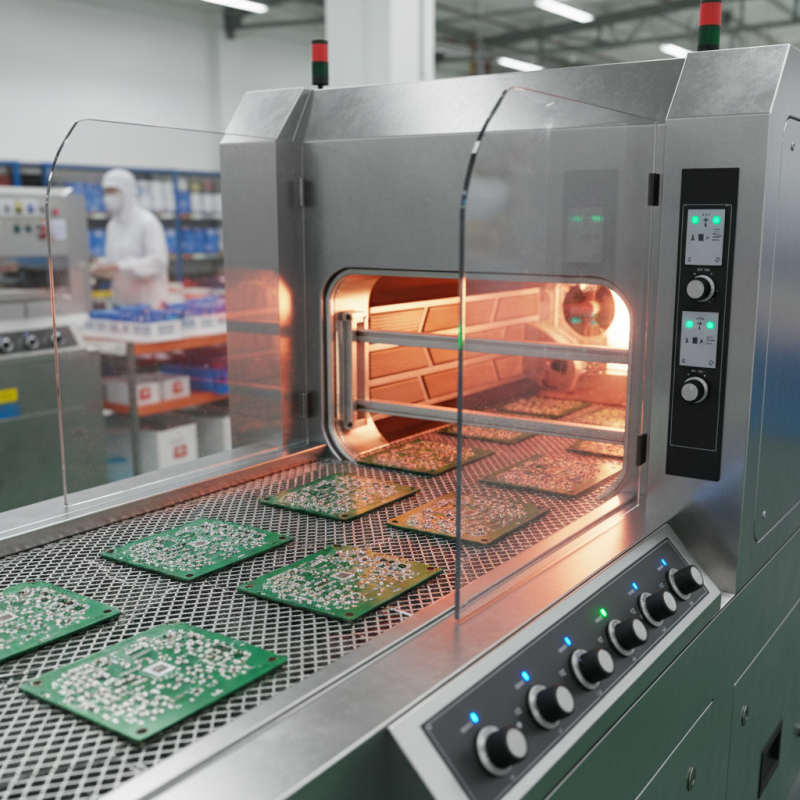

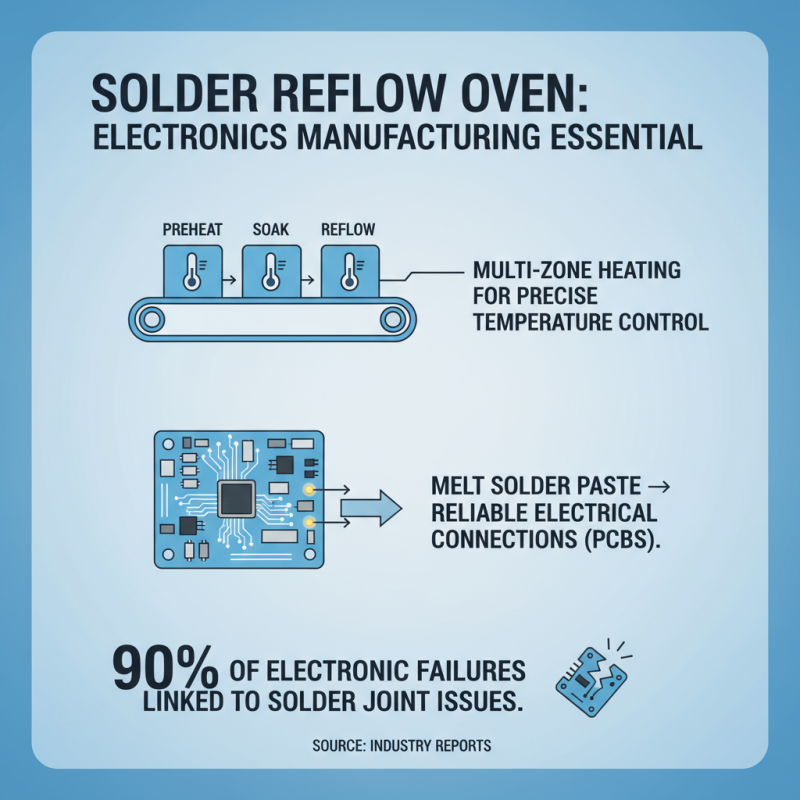
A solder reflow oven is essential in modern electronics manufacturing. It specializes in melting solder paste to create reliable electrical connections. Typically, these ovens consist of multiple heating zones. Each zone provides precise temperature control. This ensures that components adhere correctly to printed circuit boards (PCBs). According to industry reports, around 90% of electronic failures are linked to solder joint issues, highlighting the oven's significance.
Temperature accuracy is vital in solder reflow processes. An improper temperature profile can lead to cold solder joints or component damage. Data indicates that nearly 30% of assembly defects stem from inconsistent thermal profiles. The reflow oven helps to mitigate these issues, but its setup requires careful calibration. Many operators overlook this step, which can yield disappointing results.
In a world increasingly reliant on automation, solder reflow ovens are evolving. However, some still struggle with achieving optimal production speeds. Achieving a perfect balance between speed and quality remains a challenge for many manufacturers. Defects during the reflow process can lead to costly rework. Each mistake can impact overall operational efficiency and profitability, prompting manufacturers to reassess their processes continually.
A solder reflow oven is essential in electronics manufacturing. It uses heat to melt solder paste, creating strong connections between electronic components and circuit boards. Understanding its mechanism can enhance your soldering skills.
The process begins with placing a PCB loaded with components into the oven. The oven gradually heats up. At first, the temperature increases slowly to avoid thermal shock. Components need a gentle approach. The next stage is preheating, allowing solder paste to become tacky. This ensures components stay in place.
Next, the oven reaches the reflow temperature. Solder melts and flows, bonding the components to the PCB. This phase is crucial. Too high a temperature can damage parts. Too low may result in weak joints. After a brief cooling, the solder solidifies.
Tips: Always check the oven's profile settings. Each PCB might require different conditions. Take notes on failed attempts. Reflecting on what went wrong helps improve future processes.
The final cooling phase is significant. It stabilizes the soldered connections. A common issue is uneven cooling, which can lead to defects. Monitoring this process is vital. A little deviation can lead to a lot of problems down the road.
This chart illustrates the temperature profile of a typical solder reflow process. It captures the critical stages: Preheat, Soak, Reflow, and Cooling, showcasing how temperatures change during the process.
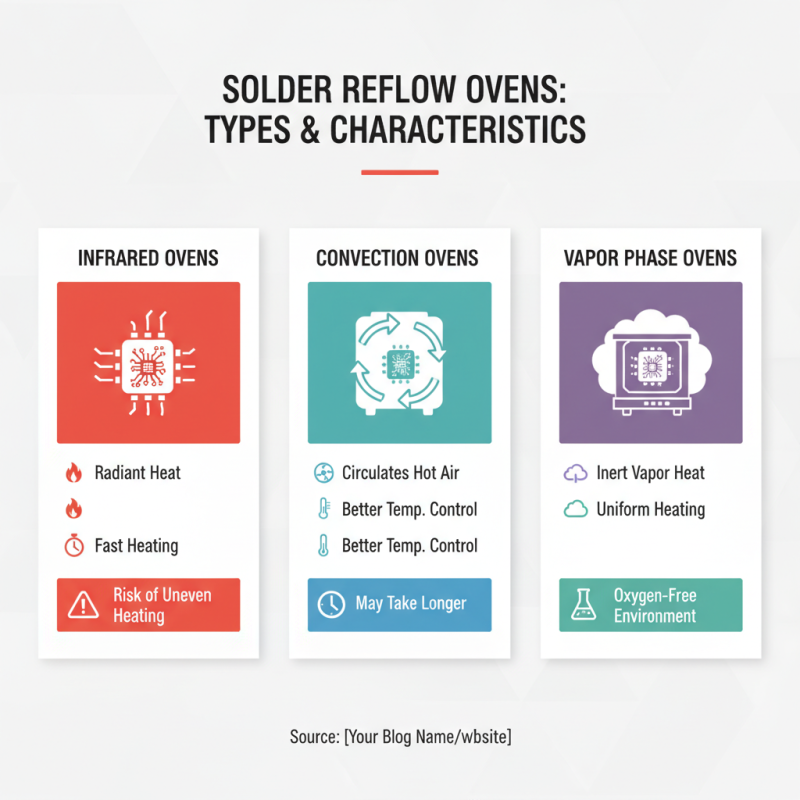
Solder reflow ovens come in different types, each suited for specific applications. The most common types include infrared, convection, and vapor phase ovens. Infrared ovens use radiant heat to melt solder paste. They are fast but can create uneven heating. Convection ovens circulate hot air, providing better temperature control. However, they may take longer to achieve the desired effect.
Vapor phase ovens are unique. They heat components using boiling liquid, which envelops them in vapor. This method ensures uniform heating but can be more complex to operate. Each type has its pros and cons, and choosing the right option can be challenging. Understanding your specific needs is crucial.
In practice, you might face issues, like overheating or insufficient solder joint quality. It’s essential to monitor the process closely. Sometimes, a quick adjustment can make a significant difference. Reflecting on your choice of oven and its settings could lead to better results in the long run.
A solder reflow oven is essential in electronics manufacturing. It provides the heat needed to melt solder and create strong connections. Understanding its key components helps in optimizing its performance.
The heating chamber is the heart of the oven. It regulates temperature and allows for controlled heating profiles. A good chamber ensures uniform heat distribution. However, some ovens struggle with hot and cold spots. This inconsistency can lead to poor solder joints. Accurate temperature control is critical.
Another important component is the conveyor system. It transports PCBs through different heating zones. The speed of the conveyor impacts the soldering process. A slow speed may overheat components, while too fast can lead to incomplete soldering. The balance is often hard to achieve. Observing and adjusting the conveyor speed is necessary for better results. Proper maintenance of these components is vital for consistent performance.
A solder reflow oven is essential in electronics manufacturing. It uses heat to melt solder, creating strong connections between components. However, several issues can arise during operation.
One common problem is uneven heating. This can lead to poor solder joints. If some areas of a PCB are too hot, components may be damaged. On the other hand, if they're too cool, the solder won't melt properly. Regular calibration of the oven's temperature settings can help overcome this challenge.
Another issue is contamination. Dust and residue can affect solder quality. Keeping the oven clean is vital for optimal performance. Regular maintenance, including checking fans and cleaning filters, can prevent overheating. Operators should routinely inspect the machinery for potential wear and tear. Neglecting these simple practices can lead to significant downtime and costly repairs.